Names of Computer Internal Parts in English
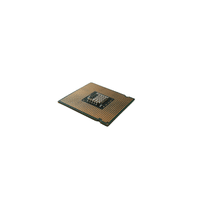
- CPU
- Processor
- Motherboard
- Chipset
- RAM
- ROM
- Cache
- Heatsink
- Fan
- PowerSupply
- Transformer
- Rectifier
- Capacitor
- Resistor
- Transistor
- Diode
- Inductor
- Crystal
- Socket
- Slot
Top 100 Computer Internal Parts with Pictures
- CPU
The main part of a computer that thinks and works on instructions, just like the brain controls the body.

- Processor
An electronic chip inside the CPU that performs calculations and makes decisions for the computer.

- Motherboard
The large main board that holds and connects all computer parts so they can communicate with each other.

- Chipset
A group of small controllers on the motherboard that manage how data moves between the CPU, memory, and devices.

- RAM
Temporary memory that stores data the computer is using right now, allowing fast work and smooth performance.

- ROM
Permanent memory that keeps important instructions needed to start the computer, even when power is off.

- Cache
Very fast memory inside or near the CPU that stores frequently used data to speed up processing.

- Heatsink
A metal part that absorbs and spreads heat away from the processor to prevent overheating.

- Fan
- A cooling device that moves air to remove heat from internal computer parts.

- Power Supply
A unit that changes electricity from the wall into safe power that computer parts can use.

- Transformer
An electrical device that increases or decreases voltage to protect electronic components.

- Rectifier
A circuit that converts alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) for electronic use.

- Capacitor
A small component that stores and releases electrical energy to keep power steady.

- Resistor
A component that controls the flow of electric current to protect circuits from damage.

- Transistor
A tiny switch that controls signals and power inside electronic devices.

- Diode
A component that allows electric current to flow in only one direction.

- Inductor
A coil that stores energy in a magnetic field and helps control current changes.

- Socket
A holder on the motherboard where the processor or chip is placed securely.

- Slot
An opening on the motherboard used to insert expansion cards or memory modules.

List of Computer Internal items
- Bus
- BIOS
- UEFI
- Firmware
- Battery
- CMOS
- HardDrive
- Platter
- Spindle
- Actuator
- ReadHead
- WriteHead
- SSD
- Controller
- NAND
- Flash
- GPU
- GraphicsCard
- VRAM
- Shader
20 Names of Computer Internal Parts in English with Pictures
- Bus
The communication path that carries data, power, and signals between computer parts.

- BIOS
A basic program stored on the motherboard that helps start the computer and check hardware.

- UEFI
A modern replacement for BIOS that starts the computer faster and supports new hardware features.

- Firmware
Built-in software that controls how a hardware device works at a basic level.

- Battery
A small power source that keeps system settings saved when the computer is turned off.

- CMOS
A memory chip that stores date, time, and hardware settings for the computer.

- Hard Drive
A storage device that saves data using spinning disks and magnetic technology.

- Platter
A circular disk inside a hard drive where data is stored in magnetic form.

- Spindle
The central rod that holds platters and spins them at high speed.

- Actuator
A moving arm that positions the read and write heads over the platter.

- Read Head
A tiny component that reads data from the surface of the hard drive.

- Write Head
A small part that records data onto the hard drive platter.

- SSD
A fast storage device that saves data using electronic memory instead of spinning parts.

- Controller
A chip that manages how data is stored, read, and written in storage devices.

- NAND
A type of memory technology used in SSDs to store data efficiently.

- Flash
Non-volatile memory that keeps data even when power is removed.

- GPU
A processor designed to handle images, videos, and visual effects quickly.

- Graphics Card
A hardware component that produces images and sends them to the display.

- VRAM
Special memory on the graphics card that stores image and video data.

- Shader
A small program that controls how colors, light, and effects appear in graphics.

Explore Computer Internal Parts Names in English
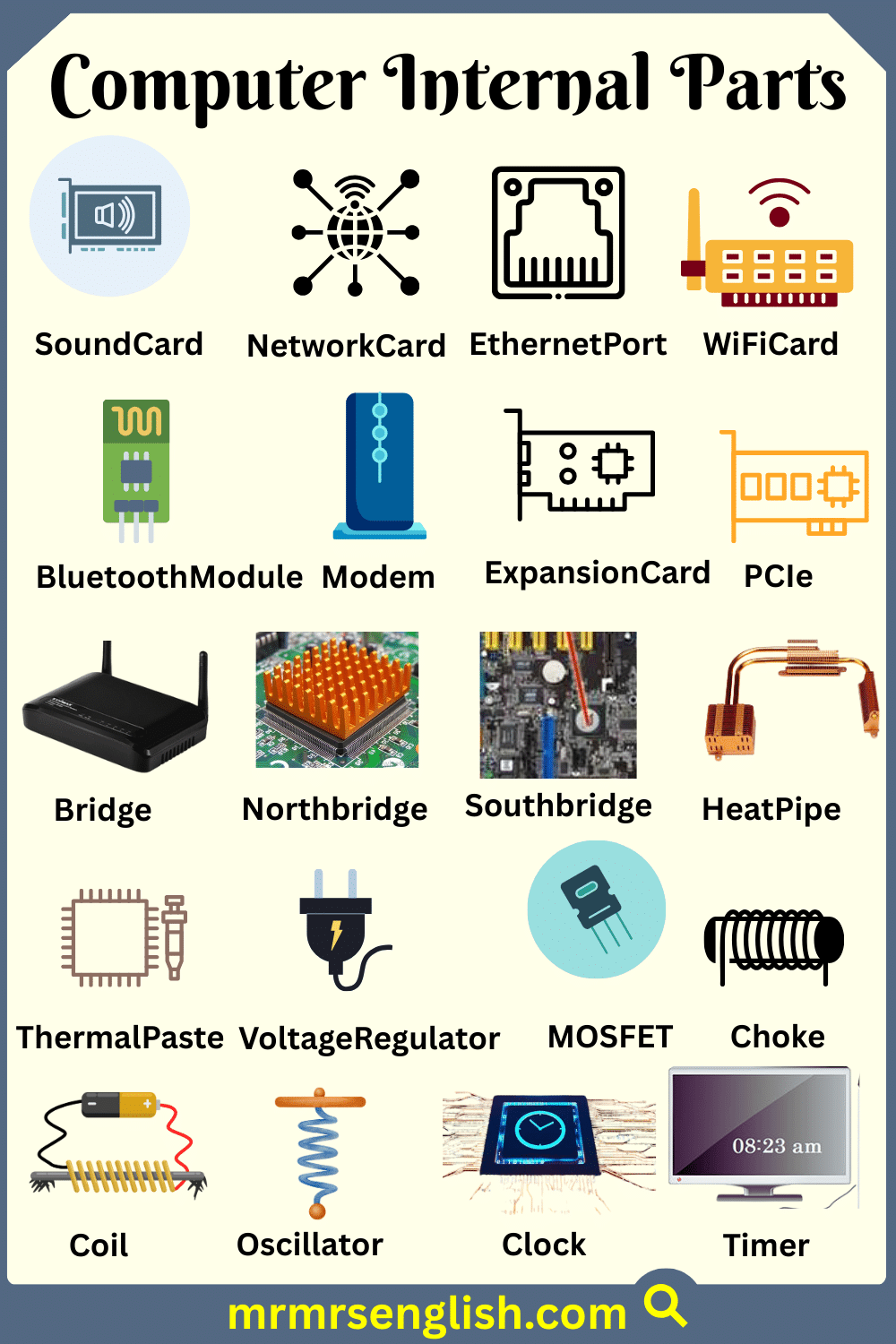
- SoundCard
- NetworkCard
- EthernetPort
- WiFiCard
- BluetoothModule
- Modem
- ExpansionCard
- PCIe
- Bridge
- Northbridge
- Southbridge
- HeatPipe
- ThermalPaste
- VoltageRegulator
- MOSFET
- Choke
- Coil
- Oscillator
- Clock
- Timer
List of Computer Internal Parts with Pictures
- Sound Card
A component that processes audio so the computer can play sounds and record voices clearly.

- Network Card
Hardware that allows a computer to connect to a network and share data with other devices.

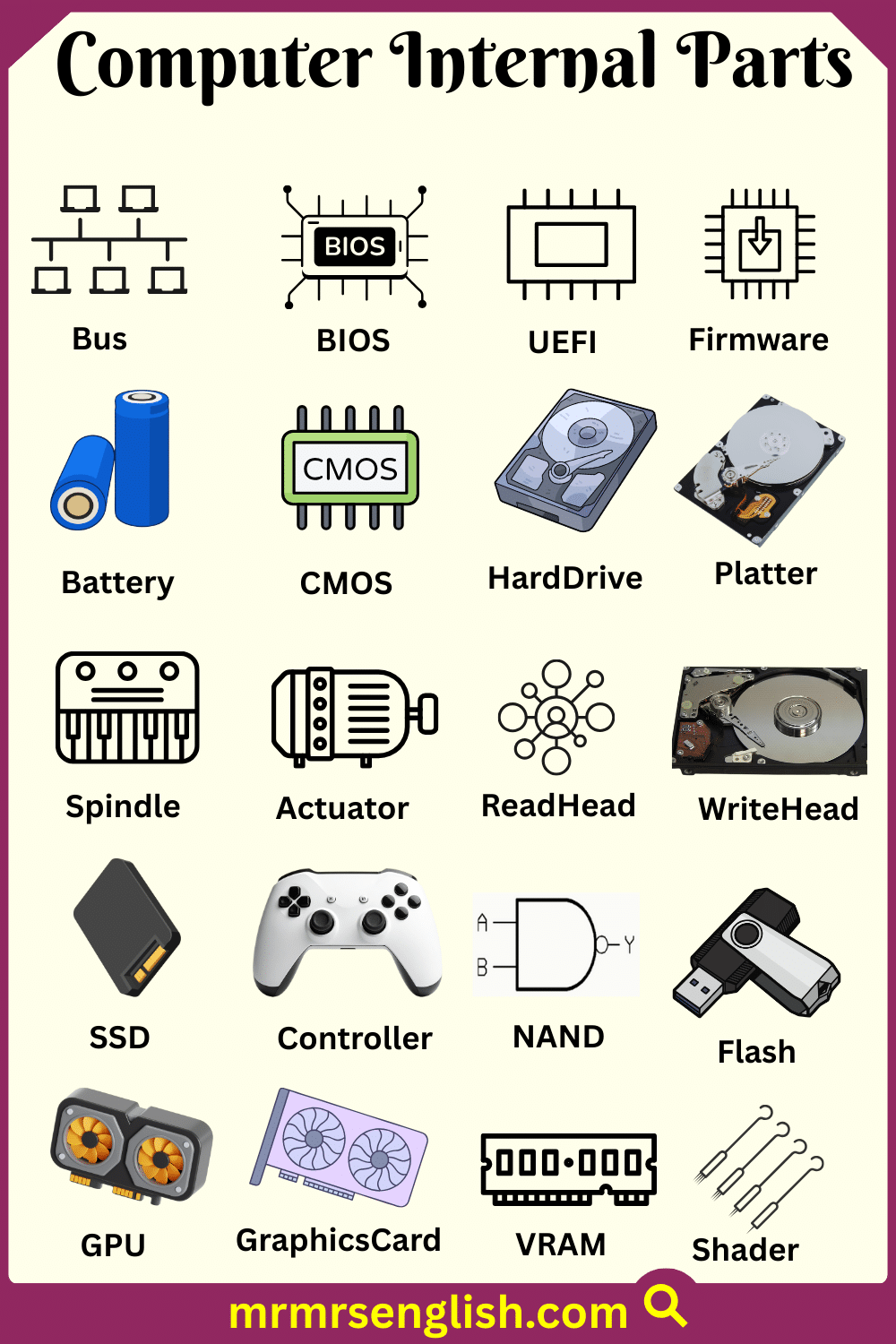
- Ethernet Port
A socket where a network cable is plugged in to provide a fast and stable internet connection.

- Wi-Fi Card
A device that lets a computer connect to wireless networks without using cables.

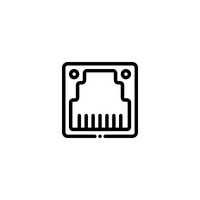
- Bluetooth Module
A small unit that enables short-range wireless communication with nearby devices.

- Modem
A device that converts internet signals so data can travel between the computer and service provider.

- Expansion Card
An add-on board used to increase a computer’s abilities, such as sound, video, or networking.

- PCIe
A high-speed connection slot on the motherboard for graphics cards and other expansion cards.

- Bridge
A controller that helps different parts of the computer communicate with each other.

- Northbridge
A chipset part that handled fast connections between the CPU, memory, and graphics.

- Southbridge
A chipset part that managed slower components like USB, audio, and storage devices.

- Heat Pipe
A sealed tube that transfers heat away from hot components to keep them cool.

- Thermal Paste
A soft material placed between a chip and heatsink to improve heat transfer.

- Voltage Regulator
A circuit that supplies steady and safe voltage to sensitive components.

- MOSFET
An electronic switch that controls power flow efficiently inside circuits.

- Choke
A component that filters electrical noise and smooths current flow.

- Coil
A wound wire that stores energy in a magnetic field and controls current changes.

- Oscillator
A circuit that creates regular electrical signals for timing purposes.

- Clock
A signal that sets the speed and rhythm of computer operations.

- Timer
A circuit that measures time delays and controls when actions occur.

Types of Computer Part
- Backplane
- Daughterboard
- RibbonCable
- SATA
- IDE
- PowerConnector
- DataConnector
- Header
- Jumper
- Switch
- Fuse
- Relay
- Sensor
- Thermistor
- Photodiode
- Microcontroller
- Coprocessor
- Accelerator
- FPGA
- ASIC
Names of Computer Internal Parts with Images
- Backplane
A large circuit board that holds and connects many other boards so they can share power and signals.

- Daughterboard
A small extra board that plugs into a main board to add new features or functions.

- Ribbon Cable
A flat cable made of many thin wires used to connect parts inside electronic devices.

- SATA
A modern connection used to link hard drives or SSDs to the motherboard for fast data transfer.

- IDE
An older type of data cable used to connect hard drives and optical drives in early computers.

- Power Connector
A connector that delivers electrical power from the supply to a device or component.

- Data Connector
A connector that allows information to move between electronic parts.

- Header
A row of metal pins on a board used to attach cables, buttons, or small devices.

- Jumper
A tiny removable piece that changes hardware settings by connecting pins.

- Switch
A device that controls whether electricity flows or stops in a circuit.

- Fuse
A safety part that breaks the circuit when too much current flows.

- Relay
An electrically controlled switch that lets a small signal control a larger load.

- Sensor
A device that detects changes like heat, light, or movement and sends a signal.

- Thermistor
A component whose resistance changes with temperature.

- Photodiode
A light-sensitive component that produces an electrical response when exposed to light.

- Microcontroller
A small computer chip used to control machines, tools, and electronic systems.

- Coprocessor
A helper processor that supports the main CPU by handling special tasks.

- Accelerator
Special hardware designed to make certain operations run faster.

- FPGA
A programmable chip that can be customized to perform specific hardware tasks.

- ASIC
A chip built for one specific job, offering high speed and efficiency.

Internal Part of a Computer
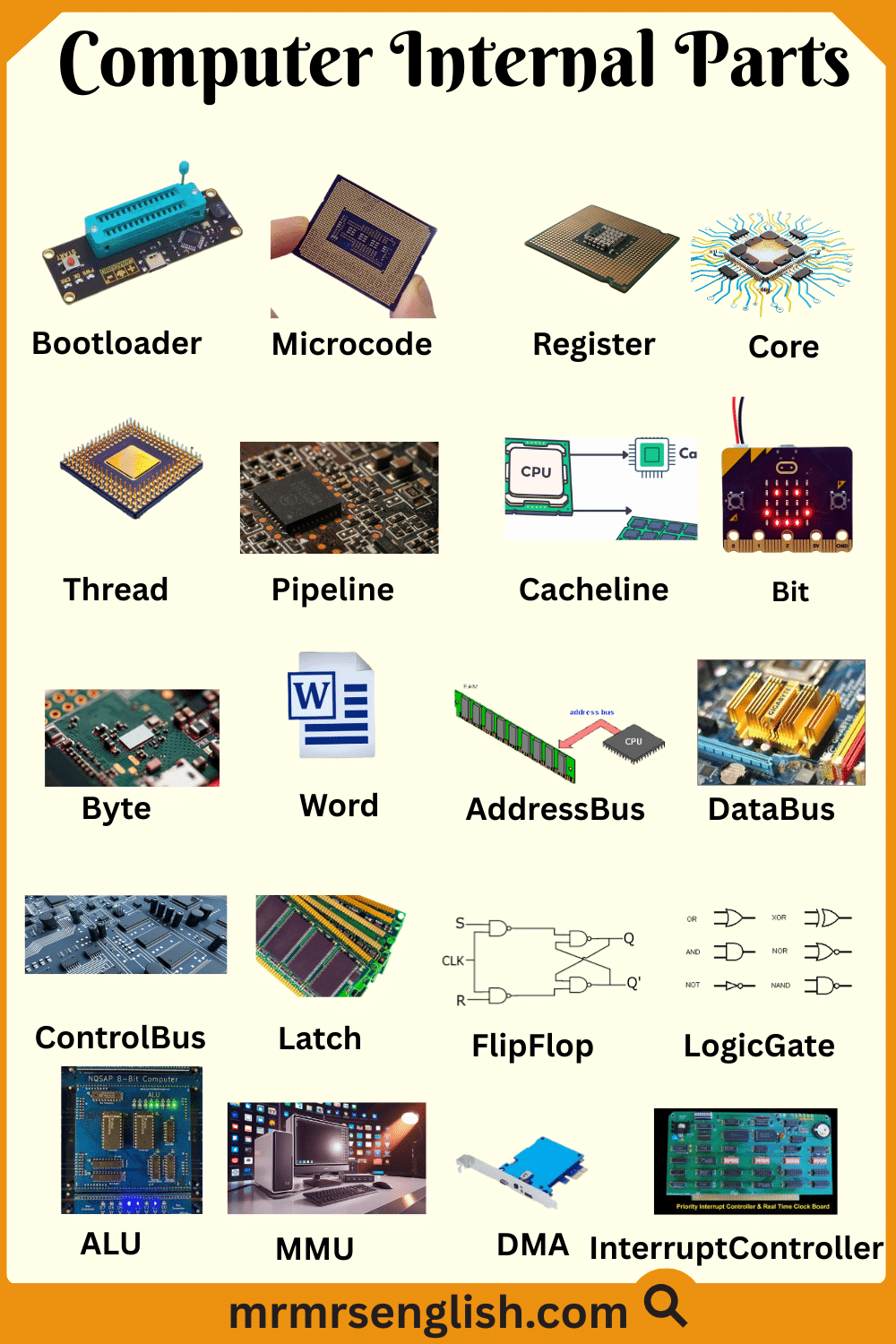
- Bootloader
- Microcode
- Register
- Core
- Thread
- Pipeline
- Cacheline
- Bit
- Byte
- Word
- AddressBus
- DataBus
- ControlBus
- Latch
- FlipFlop
- LogicGate
- ALU
- MMU
- DMA
- InterruptController
Computer Internal Parts with Images and Names
- Bootloader
A small program that starts the computer and loads the operating system into memory.

- Microcode
Low-level instructions inside the CPU that control how hardware instructions are carried out.

- Register
A very small and fast storage area inside the CPU used to hold data temporarily.

- Core
An independent processing unit inside a processor that can run programs on its own.

- Thread
A single path of execution that allows a program to do tasks in parallel.

- Pipeline
A method where instruction steps are processed in stages to improve speed.

- Cacheline
A fixed-size block of data moved between cache and main memory together.

- Bit
The smallest unit of data that can be either 0 or 1.

- Byte
A group of eight bits used to represent a single character or value.

- Word
A fixed-sized piece of data that a processor handles at one time.

- Address Bus
A set of lines used to specify the location of data in memory.

- Data Bus
A pathway that carries actual data between components.

- Control Bus
A set of lines that carry commands and control signals in a system.

- Latch
A simple memory element that stores a value while enabled.

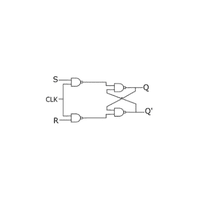
- Flip-Flop
A basic memory circuit that stores one bit and changes state on a signal.

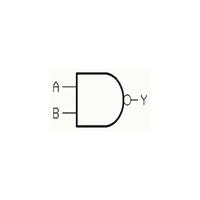
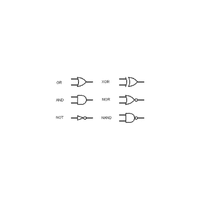
- Logic Gate
An electronic circuit that performs basic logical operations like AND or OR.

- ALU
The part of the CPU that performs arithmetic and logical calculations.

- MMU
A unit that manages memory access and translates addresses.

- DMA
A method that allows devices to transfer data without using the CPU.

- Interrupt Controller
A component that manages and prioritizes interrupt signals sent to the CPU

Learn more Helpful articles







































Leave a Comment