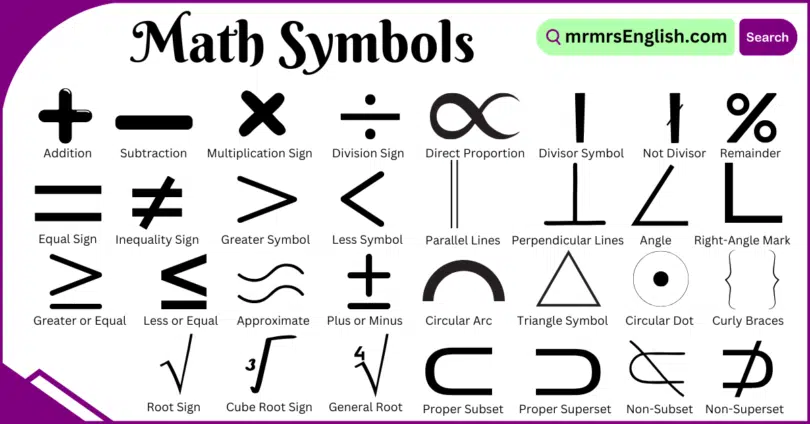
Math symbols are simple signs used to show numbers, operations, or relationships in mathematics. These symbols help us solve problems quickly and easily. For example, the plus sign (+) is used for addition, and the equals sign (=) shows that two values are the same. Some common math symbols names in English for example, Addition (+), Subtraction (−), Multiplication Sign (×), Division Sign (÷), Equal Sign (=), Inequality Sign (≠), Greater Symbol (>). In this article, I have covered Math Symbols Names in English and Their Pictures. All are given below, let’s learn…
Math Symbols Names
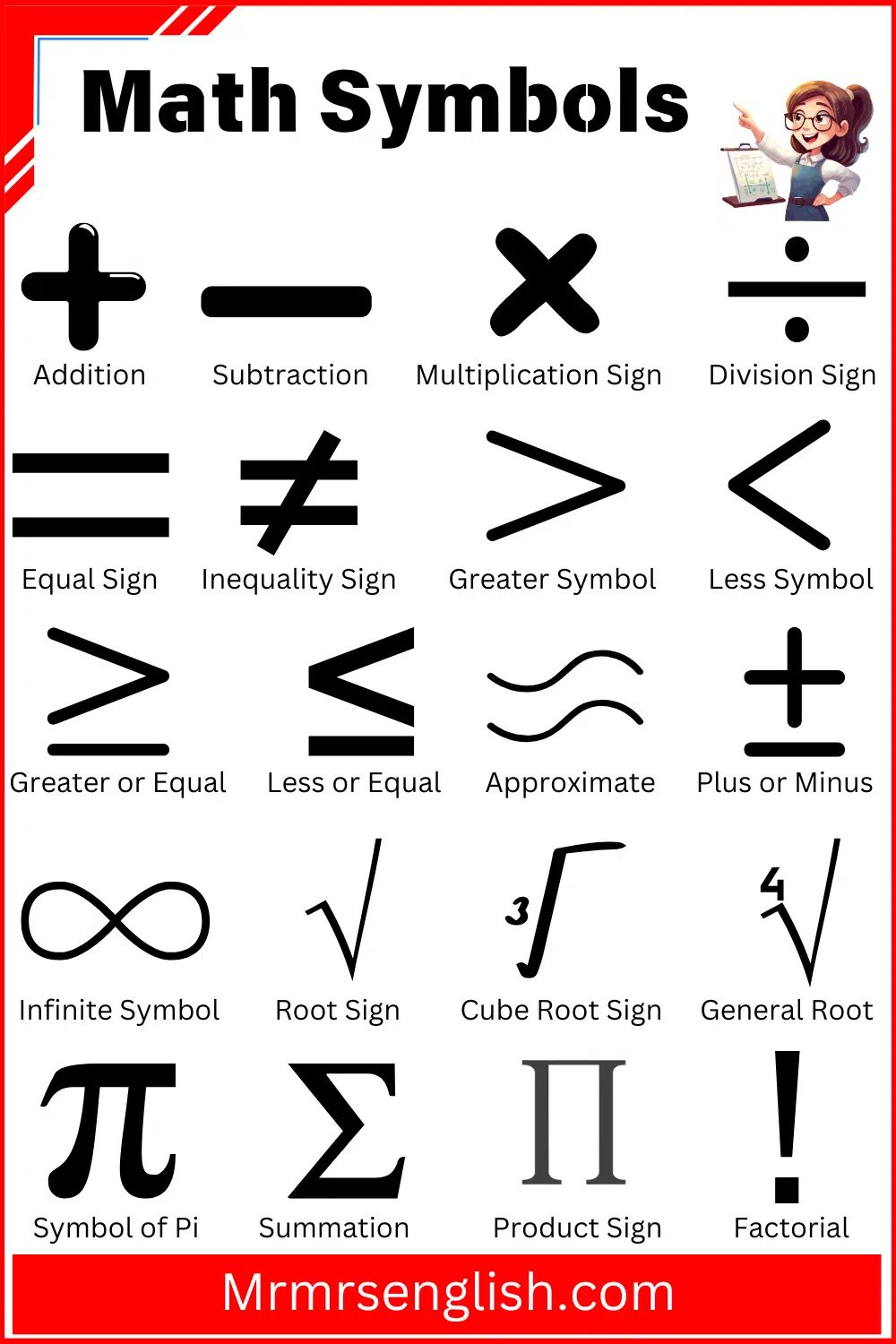
- Addition (+)
- Subtraction (−)
- Multiplication Sign (×)
- Division Sign (÷)
- Equal Sign (=)
- Inequality Sign (≠)
- Greater Symbol (>)
- Less Symbol (<)
- Greater or Equal Symbol (≥)
- Less or Equal Symbol (≤)
- Approximate Symbol (≈)
- Plus or Minus (±)
- Infinite Symbol (∞)
- Root Sign (√)
- Cube Root Sign (∛)
- General Root (∜)
- Symbol of Pi (π)
- Summation Symbol (∑)
- Product Sign (∏)
- Factorial Symbol (!)
Names of Math Symbols with Pictures
- Addition (+):
Combines two or more numbers to get their total.

- Subtraction (−):
Finds the difference by removing one number from another.

- Multiplication Sign (×):
Represents repeated addition of a number.

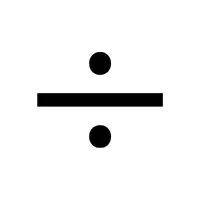
- Division Sign (÷):
Splits a number into equal parts or groups.
- Equal Sign (=):
demonstrates that the values of two expressions are equal.
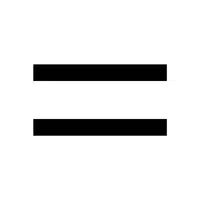
- Inequality Sign (≠):
Indicates that two values are not equal.
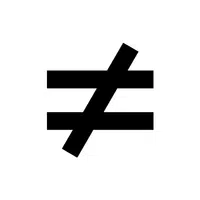
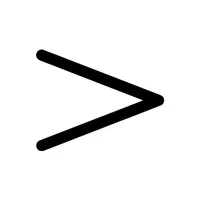
- Greater Symbol (>):
Compares two values, showing the first is larger.
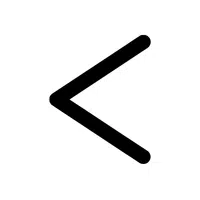
- Less Symbol (<):
shows that the first value is smaller when two are compared.
- Greater or Equal Symbol (≥):
Shows a value is either greater than or equal to another.
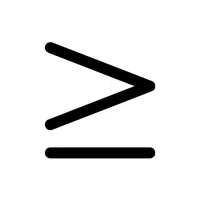
- Less or Equal Symbol (≤):
Shows a value is either less than or equal to another.

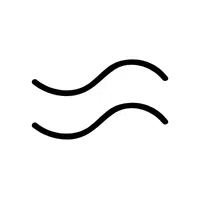
- Approximate Symbol (≈):
demonstrates that two values are almost but not quite equal.
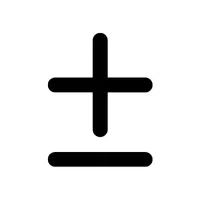
- Plus or Minus (±):
Represents two possible values, one positive and one negative.
- Infinite Symbol (∞):
Represents a value without limits or an unending quantity.

- Root Sign (√):
Finds the number that multiplies by itself to make the given value.
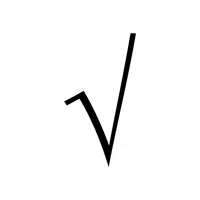
- Cube Root Sign (∛):
Finds the number that multiplies by itself three times to make the given value.

- General Root (∜):
Finds a number raised to any given power to match the original value.
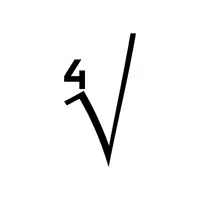
- Symbol of Pi (π):
Represents the ratio of a circle’s circumference to its diameter, approximately 3.14.

- Summation Symbol (∑):
Adds up a series of numbers or terms.

- Product Sign (∏):
Multiplies a series of numbers or terms together.

- Factorial Symbol (!):
Multiplies all whole numbers from a given number down to one.

Symbols Names list
- Direct Proportion (∝)
- Divisor Symbol (|)
- Not Divisor (∤)
- Remainder Symbol (%)
- Parallel Lines (∥)
- Perpendicular Lines (⊥)
- Angle Symbol (∠)
- Right-Angle Mark (∟)
- Circular Arc (⌒)
- Triangle Symbol (△)
- Circular Dot (⊙)
- Curly Braces ( { } )
- Proper Subset (⊂)
- Proper Superset (⊃)
- Non-Subset (⊄)
- Non-Superset (⊅)
- Null Set (∅)
- Membership (∈)
- Non-Membership (∉)
- Set Union (∪)
Math Symbols and Their Pictures
- Direct Proportion (∝):
Shows that two quantities increase or decrease together at the same rate.

- Divisor Symbol (|):
shows that there is no residual when one integer divides another.

- Not Divisor (∤):
Represents that one number does not divide another exactly.

- Remainder Symbol (%):
Shows the leftover part after division.

- Parallel Lines (∥):
Represents two lines that never meet, no matter how extended.
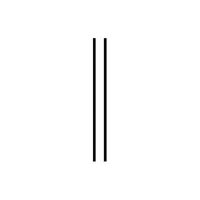
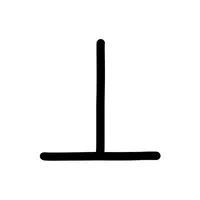
- Perpendicular Lines (⊥):
Indicates two lines meeting at a 90-degree angle.
- Angle Symbol (∠):
Denotes the space between two intersecting lines or rays.
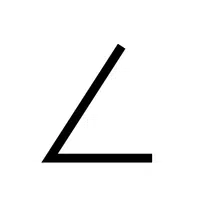
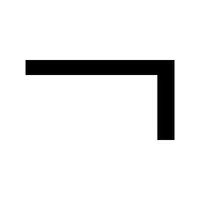
- Right-Angle Mark (∟):
Specifies an exact 90-degree angle.
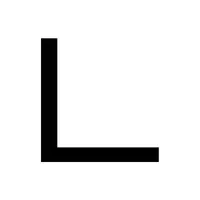
- Circular Arc (⌒):
Represents a curved part of a circle’s circumference.

- Triangle Symbol (△):
represents a polygon with three sides.

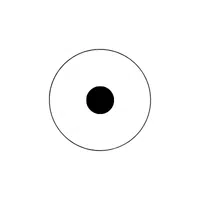
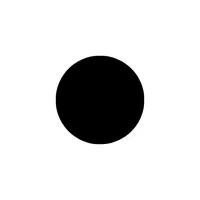
- Circular Dot (⊙):
Represents the center point of a circle.
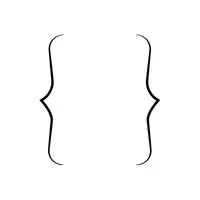
- Curly Braces ({ }):
Encloses elements in a set or group.
- Proper Subset (⊂):
Indicates that one set is fully contained within another but is not equal to it.

- Proper Superset (⊃):
Shows that one set contains all elements of another but is not equal to it.

- Non-Subset (⊄):
Indicates that one set is not part of another.
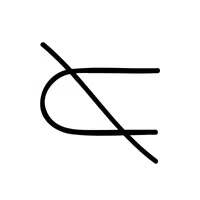
- Non-Superset (⊅):
Shows that one set does not completely contain another.
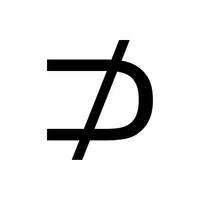
- Null Set (∅):
Represents an empty set with no elements.

- Membership (∈):
Indicates that an element belongs to a set.

- Non-Membership (∉):
Shows that an element does not belong to a set.

- Set Union (∪):
blends every distinct component from two or more sets.

All Type of Math Symbols list
- Set Intersection (∩)
- Complement of Set (′)
- Modulus or Absolute (|x|)
- Single Integral (∫)
- Double Integral Notation (∬)
- Triple Integral Notation (∭)
- Derivative Symbol (∂)
- Nabla Operator (∇)
- Symbol for Gradient (∇f)
- Change Symbol (Δ)
- Vector Cross Product (×)
- Vector Dot Product (·)
- Square Brackets for Matrix ([ ])
- Matrix Transpose Symbol (Aᵀ)
- Sigma Notation (Σxᵢ)
- Logarithm Base-10 (log)
- Logarithm Base-e (ln)
- Exponent Base (e)
- Power Symbol (aᵇ)
- Average Symbol (x̄)
Some Basic Mathematical Symbols with Pictures
- Set Intersection (∩):
Represents common elements shared by two or more sets.

- Complement of Set (′):
indicates elements that belong to the universal set rather than a specific set.

- Modulus or Absolute (|x|):
Gives the distance of a number from zero, always positive.

- Single Integral (∫):
Calculates the area under a curve or the total sum over an interval.

- Double Integral Notation (∬):
Represents the volume under a surface in two dimensions.
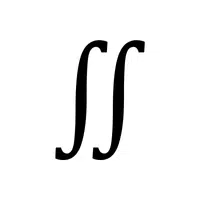
- Triple Integral Notation (∭):
Finds the volume in three-dimensional space.

- Derivative Symbol (∂):
Indicates the rate of change of a function with respect to a variable.

- Nabla Operator (∇):
Represents a vector differential operator for gradients, curls, or divergence.

- Symbol for Gradient (∇f):
Shows the direction and rate of the steepest increase of a function.
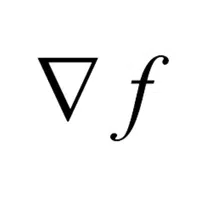
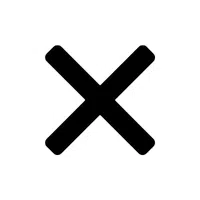
- Vector Cross Product (×):
Calculates a vector perpendicular to two given vectors.
- Vector Dot Product (·):
Finds a scalar value by multiplying two vectors and summing their components.
- Square Brackets for Matrix ([ ]):
Encloses numbers or elements in rows and columns to form a matrix.
![Square Brackets for Matrix ([ ])](http://mrmrsenglish.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/Square-Brackets-for-Matrix-.png.webp)
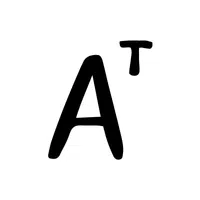
- Matrix Transpose Symbol (Aᵀ):
Represents flipping a matrix over its diagonal, swapping rows with columns.
- Sigma Notation (Σxᵢ):
Summarizes a series of numbers or terms.
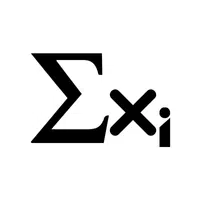
- Logarithm Base-10 (log):
Finds the power to which 10 must be raised to get a given number.
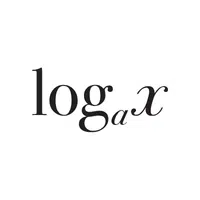
- Logarithm Base-e (ln):
Determines the power to which the base e (≈2.718) must be raised to get a number.
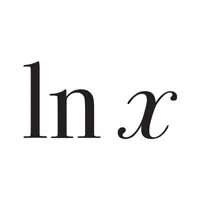
- Exponent Base (e):
The constant approximately equal to 2.718, used in natural growth or decay functions.
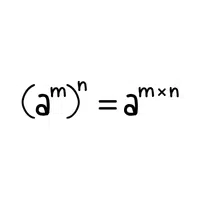
- Power Symbol (aᵇ):
Represents a number (a) raised to the power of another number (b).

- Average Symbol (x̄):
Indicates the mean value of a set of numbers, calculated as the sum divided by the count.
List of All Math Symbols
- Power Symbol (aᵇ)
- Average Symbol (x̄)
- Variance Indicator (σ²)
- Standard Deviation Marker (σ)
- Symbol for Probability (P)
- Permutations Indicator (nPr)
- Limit Marker (lim)
- Function Representation (f(x))
- Imaginary Number Symbol (i)
- Complex Number Format (a + bi)
- Real Component (Re(z))
- Imaginary Component (Im(z))
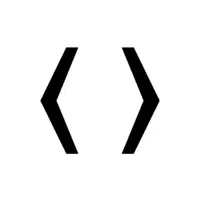
- Vector Angle Brackets (⟨ ⟩)
- Conditional Probability Symbol (P(A|B))
- Equation Line (y = mx + b)
- Polynomial Form (P(x))
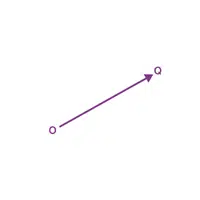
- Vector Representation (→)
- Expected Value Symbol (E(X))
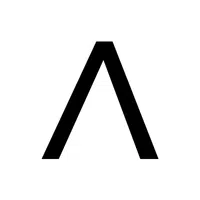
- Logical Conjunction (∧)
- Logical Disjunction (∨)
- Logical Negation (¬)





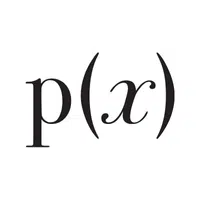
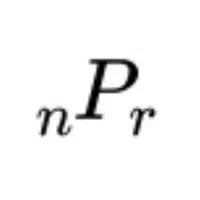
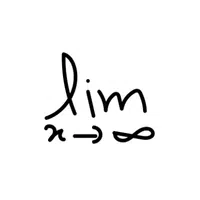


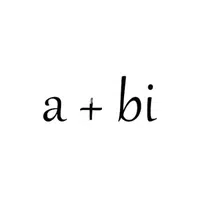
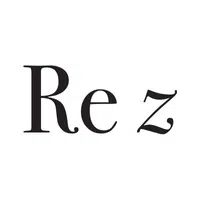
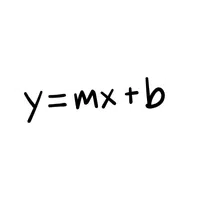
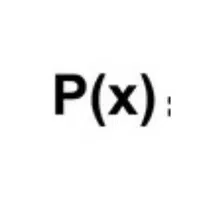
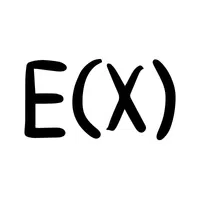








Leave a Comment