Symbols are an important part of our daily life and communication. They are small signs or marks that carry big meanings and are used in writing, mathematics, science, technology, and even on the internet. Each symbol has its own name and purpose, which helps us understand and share information quickly. For example, the @ symbol is used in email addresses, while the % symbol shows percentage. Learning the names and uses of symbols in English is very helpful for students, learners, and professionals. In this article, we will learn symbols names and their uses in English with pictures to make learning simple and effective.
100 Symbols Names in English
- @ – At symbol
- # – Hashtag
- & – Ampersand
- $ – Dollar sign
- % – Percent sign
- ^ – Caret
- & – And sign
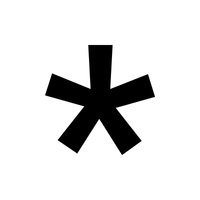
- * – Asterisk
- ( ) – Parentheses
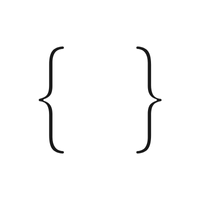
- { } – Curly braces
- [ ] – Square brackets
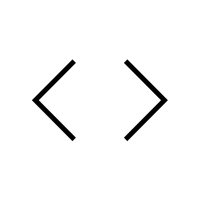
- < > – Angle brackets
- | – Vertical bar
- ~ – Tilde
- _ – Underscore
- = – Equal sign
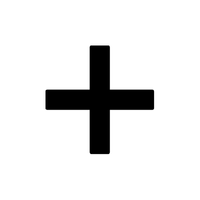
- + – Plus sign
- – – Minus sign
- / – Slash
- \ – Backslash
Symbols and their Uses in English
- @ (At Symbol):
Used in email addresses to separate the username from the domain. It’s also used in social media to mention or tag someone directly.

- # (Hashtag):
Commonly used in social media posts to categorize content by topics or trends, making it searchable under specific topics.

- & (Ampersand):
Represents the word “and” in writing and is often used in brand names or short-form text to connect ideas, such as in company names.

- $ (Dollar Sign):
Denotes currency, especially US dollars, and is used in financial contexts to indicate price or value.

- % (Percent Sign):
Represents a fraction out of 100, commonly used to show percentages in math, discounts, and data reporting.

- ^ (Caret):
Used in writing and editing to indicate where something should be inserted or in math as a symbol for exponentiation (raising a number to a power).

- *** (Asterisk)**:
Often used to indicate a footnote, correction, or emphasis in text. It can also act as a wildcard in search functions.

- ( ) (Parentheses):
Used to add extra information, clarify meaning, or group parts in math and programming.

- { } (Curly Braces):
Frequently used in programming to group statements or data together, especially in coding languages like JavaScript and Python.

- [ ] (Square Brackets):
Commonly used in texts for clarification or added information. In programming, they are used to indicate arrays or lists of data.
![[ ] (Square Brackets) Symbol Name in English](data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyB4bWxucz0iaHR0cDovL3d3dy53My5vcmcvMjAwMC9zdmciIHdpZHRoPSIyMDAiIGhlaWdodD0iMjAwIiB2aWV3Qm94PSIwIDAgMjAwIDIwMCI+PHJlY3Qgd2lkdGg9IjEwMCUiIGhlaWdodD0iMTAwJSIgc3R5bGU9ImZpbGw6I2NmZDRkYjtmaWxsLW9wYWNpdHk6IDAuMTsiLz48L3N2Zz4=)
- < > (Angle Brackets):
Used in math to represent inequalities and in HTML code to enclose tags for webpage structure.

- | (Vertical Bar):
Often used to separate options or parts in coding, or in writing to indicate choices or alternate paths.

- ~ (Tilde):
Represents approximation in math (meaning “about”) and in some contexts indicates a range. It’s also used to create special characters in programming.

- _ (Underscore):
Used in filenames or usernames to replace spaces or join words and is also a placeholder for certain symbols in programming.

- = (Equal Sign):
Indicates equality in math equations and is used to assign values in programming.

- + (Plus Sign):
Represents addition in math, is used in search engines to include specific terms, and signifies positivity or inclusion.

- – (Minus Sign):
Represents subtraction in math and is used to exclude specific terms in search engines or writing.

- / (Slash):
Used to separate alternatives, show fractions in math, and denote directory paths in file systems.

- \ (Backslash):
Common in file paths, especially on Windows operating systems, and in coding for escaping characters or special symbols.

Names of Symbols in English
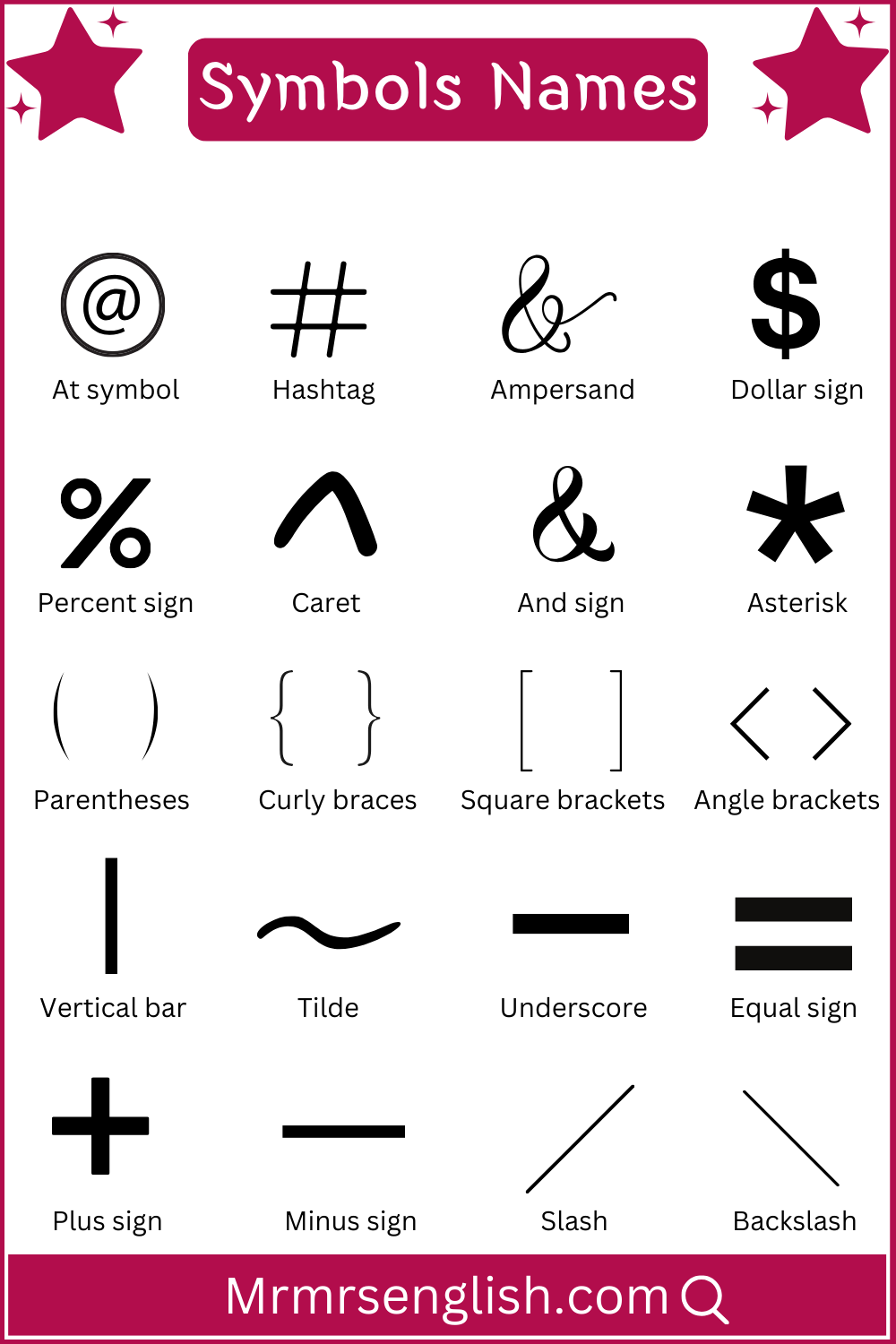
- : – Colon
- ; – Semicolon
- “ – Quotation marks
- ‘ – Apostrophe
- . – Period
- , – Comma
- ? – Question mark
- ! – Exclamation mark
- § – Section symbol
- ¶ – Paragraph symbol
- ∞ – Infinity symbol
- π – Pi symbol
- Σ – Sigma symbol
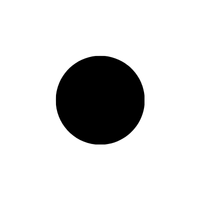
- Δ – Delta symbol
- Ω – Omega symbol
- ≈ – Approximation symbol
- ≠ – Not equal sign
- ≤ – Less than or equal to
- ≥ – Greater than or equal to
- ∑ – Summation symbol
Pictures of Symbols and their uses
- : (Colon):
Used to introduce lists, explanations, or quotes. It signals that more information is following, making it useful for clarifying ideas or organizing content.

- ; (Semicolon):
Connects related but independent ideas or separates items in a complex list. It helps improve sentence flow and readability in longer sentences.

- ” (Quotation Marks):
Encloses direct speech, quotes, or specific titles. Quotation marks emphasize spoken words, titles, or cited phrases within text.

- ‘ (Apostrophe):
Indicates possession or contractions. It shortens words (e.g., “don’t” for “do not”) and shows ownership (e.g., “Sara’s book”).

- . (Period):
Marks the end of a sentence, giving readers a pause and providing clarity to written communication.

- , (Comma):
Separates items in a list or divides clauses, adding clarity and helping structure sentences for smooth reading.

- ? (Question Mark):
Ends a question, signifying that the sentence seeks an answer. This symbol makes it clear when a response or clarification is needed.

- ! (Exclamation Mark):
Adds emphasis or shows strong emotion, such as surprise or excitement, in sentences.

- § (Section Symbol):
Common in legal and formal writing to refer to specific sections or paragraphs, making it easier to organize and reference content.

- ¶ (Paragraph Symbol):
Marks the beginning of a new paragraph in writing or in editing notes, helping with document structure and readability.

- ∞ (Infinity Symbol):
Represents the concept of endlessness or something without limits. It’s often used in mathematics and philosophy.

- π (Pi Symbol):
Denotes the mathematical constant pi (approximately 3.14), widely used in geometry to calculate circle measurements.

- Σ (Sigma Symbol):
Indicates summation or the total of a sequence, often used in mathematics, statistics, and science.

- Δ (Delta Symbol):
Represents change or difference, especially in math and science, where it is used to show variation in quantities.

- Ω (Omega Symbol):
Represents the final value in a set or the last item. In physics, it also denotes units of resistance (ohms).

- ≈ (Approximation Symbol):
Used to show an approximate value, indicating that a number is not exact but close to a given amount.

- ≠ (Not Equal Sign):
Shows that two values or expressions are different from each other, commonly used in math and logical statements.

- ≤ (Less Than or Equal To):
Indicates that a value is either less than or equal to another value. Useful in math for comparisons in equations.

- ≥ (Greater Than or Equal To):
Shows that a value is greater than or equal to another. It’s often used in inequalities and comparisons.

- ∑ (Summation Symbol):
Represents the sum of a set of values, often used in mathematics, especially in statistics to calculate totals.

Common Symbols names in English
- ∏ – Product Symbol
- √ – Square root symbol
- √ – Radical symbol
- ∂ – Partial derivative symbol
- ℘ – Weierstrass p symbol
- ℓ – Script l (literature)
- ∈ – Element of symbol
- ∉ – Not an element of symbol
- ⊂ – Subset symbol
- ⊆ – Subset or equal symbol
- ⊄ – Not a subset symbol
- ⊇ – Superset or equal symbol
- ⊃ – Superset symbol
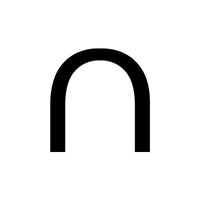
- ∩ – Intersection symbol
- ∪ – Union symbol
- ⊥ – Perpendicular symbol
- ⇒ – Implies symbol
- ⇔ – If and only if symbol
- ↔ – Right-left arrow
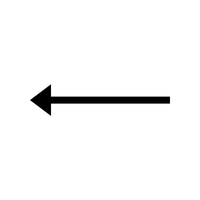
- ← – Left arrow
100 Symbols Pictures and Their Uses
- ∏ (Product Symbol):
Represents the product of a sequence of terms in mathematics. It is commonly used in formulas to show the multiplication of a range of values.

- √ (Square Root Symbol):
Indicates the square root of a number, which is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. Widely used in math to simplify calculations.

- √ (Radical Symbol):
Also known as the root symbol, it represents the square root or higher roots (like cube roots) of a number, especially in algebra and geometry.

- ∂ (Partial Derivative Symbol):
Used in calculus to represent the partial derivative, indicating how a function changes concerning one variable while keeping others constant.

- ℘ (Weierstrass p Symbol):
Refers to the Weierstrass function in mathematics, often appearing in complex analysis or advanced calculus topics.

- ℓ (Script l):
Often used to represent a specific length or measure, commonly seen in literature or math contexts for denoting a line or length variable.

- ∈ (Element of Symbol):
Shows that an item is part of a set or group, widely used in set theory to express relationships between elements and sets.

- ∉ (Not an Element of Symbol):
Indicates that an item does not belong to a specific set. Used in math to clarify which elements are not included in a given group.

- ⊂ (Subset Symbol):
Shows that all elements of one set are included within another set. It’s important in set theory for defining group relationships.

- ⊆ (Subset or Equal Symbol):
Denotes that one set is either a subset of another or identical to it, often used when comparing two sets.

- ⊄ (Not a Subset Symbol):
Indicates that one set is not fully contained within another, helping to specify boundaries in mathematical grouping.

- ⊇ (Superset or Equal Symbol):
Shows that a set includes all elements of another set or is equal to it, used in set theory to show broader inclusions.

- ⊃ (Superset Symbol):
Indicates that one set contains all elements of another set, useful for organizing sets and understanding hierarchies.

- ∩ (Intersection Symbol):
Represents the intersection or common elements shared between two sets. It’s essential in set theory for finding overlap between groups.

- ∪ (Union Symbol):
Indicates the union or combination of all elements in two sets. This symbol is used in set theory to join groups.

- ⊥ (Perpendicular Symbol):
Used in geometry to show that two lines or segments meet at a right angle, which is a 90-degree intersection.

- ⇒ (Implies Symbol):
Indicates that one statement logically leads to another, often used in logical proofs to connect cause and effect.

- ⇔ (If and Only If Symbol):
Shows that two statements are both true or both false, meaning they depend on each other. It’s vital in logic for showing bidirectional relationships.

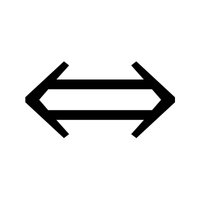
- ↔ (Right-Left Arrow):
Represents a connection or equivalence between two items, showing that they are related or interchangeable in a specific context.

- ← (Left Arrow):
Points left to indicate direction or a return in a process, commonly used in diagrams or flowcharts to show movement or steps in a sequence.

Names of Symbols in English
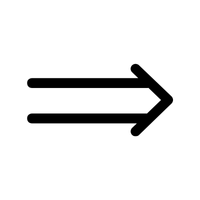
- → – Right arrow
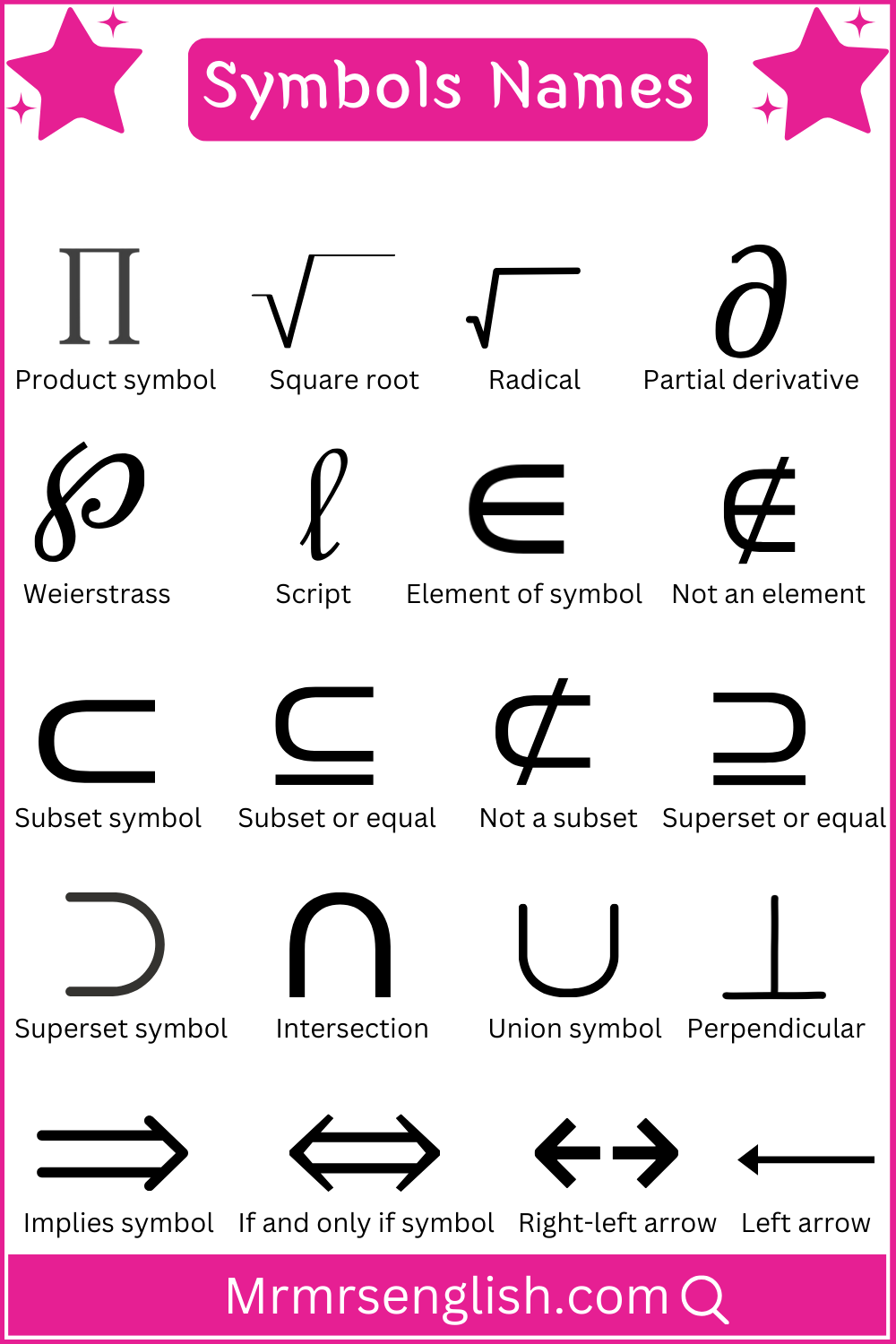
- ↑ – Upward arrow
- ↓ – Downward arrow
- ↗ – Northeast arrow
- ↖ – Northwest arrow
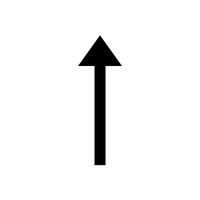
- ↙ – Southwest arrow
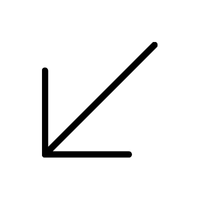
- ↘ – Southeast arrow
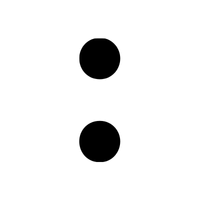
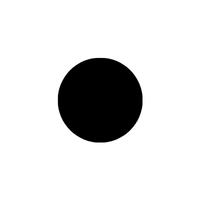
- • – Bullet point
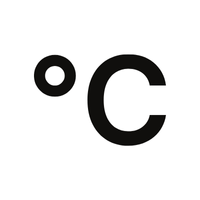
- ◦ – Degree symbol
- © – Copyright symbol
- ® – Registered trademark symbol
- ™ – Trademark symbol
- € – Euro symbol
- £ – Pound symbol
- ¥ – Yen symbol
- ₣ – Franc symbol
- ₤ – British pound symbol
- ₹ – Indian Rupee symbol
- ₱ – Peso symbol
- ♻ – Recycling symbol
Symbols names in English and pictures
- → (Right Arrow):
Points to the right, often used to show direction, progression, or movement in a sequence, commonly seen in diagrams and instructions.

- ↑ (Upward Arrow):
Indicates an upward direction, often used in instructions, maps, or to symbolize growth or increase in values.

- ↓ (Downward Arrow):
Shows a downward direction, symbolizing decrease, reduction, or a step down in instructions and charts.

- ↗ (Northeast Arrow):
Points diagonally up and to the right, used to indicate movement or direction toward the northeast.

- ↖ (Northwest Arrow):
Points diagonally up and to the left, showing movement or direction toward the northwest.

- ↙ (Southwest Arrow):
Points diagonally down and to the left, indicating movement or direction toward the southwest.

- ↘ (Southeast Arrow):
Points diagonally down and to the right, showing movement or direction toward the southeast.

- • (Bullet Point):
Marks items in a list, helping to separate and organize points for clear, structured information.

- ◦ (Degree Symbol):
Represents degrees, used in measurements of temperature, angles, and geographical coordinates.

- © (Copyright Symbol):
Indicates legal ownership of creative content, such as books, music, and art, protecting the creator’s rights.

- ® (Registered Trademark Symbol):
Shows that a name, logo, or slogan is officially registered as a trademark, protecting it from unauthorized use.

- ™ (Trademark Symbol):
Indicates that a name, logo, or slogan is used as a trademark, even if it’s not yet registered, marking it as the creator’s unique property.

- € (Euro Symbol):
Represents the currency used in many European Union countries, particularly in financial transactions and pricing.

- £ (Pound Symbol):
Signifies the British currency (pound sterling), used in finance and pricing primarily in the UK.

- ¥ (Yen Symbol):
Represents the Japanese currency yen, commonly seen in financial transactions involving Japan.

- ₣ (Franc Symbol):
Historically used to represent the French franc and other franc-based currencies, seen mainly in historical contexts.

- ₤ (British Pound Symbol):
Another symbol for the British pound, though less commonly used today, with similar uses as the £ sign.

- ₹ (Indian Rupee Symbol):
Represents the Indian currency rupee, commonly used in transactions and pricing in India.

- ₱ (Peso Symbol):
Denotes the peso, a currency used in countries like the Philippines and Mexico, commonly seen in prices and financial contexts.

- ♻ (Recycling Symbol):
Indicates that an item is recyclable or made from recycled materials, promoting environmental awareness and responsible disposal.

List of Symbols in English
- ☮ – Peace symbol
- ☯ – Yin Yang symbol
- ✝ – Christian cross symbol
- ✡ – Star of David symbol
- ☪ – Star and crescent symbol
- ✿ – Flower symbol
- ☀ – Sun symbol
- ☁ – Cloud symbol
- ☂ – Umbrella symbol
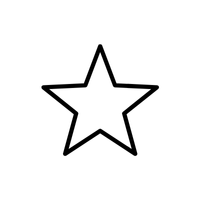
- ★ – Star symbol
- ☆ – Hollow star symbol
- ✦ – Sparkle symbol
- ❄ – Snowflake symbol
- ♠ – Spade symbol
- ♣ – Club symbol
- ♥ – Heart symbol
- ♒ – Aquarius symbol
- ♓ – Pisces symbol
- ♈ – Aries symbol
- ♉ – Taurus symbol
All Symbols names with pictures in English
- ☮ (Peace Symbol):
A symbol of harmony and anti-war messages often used to represent peace in social and cultural contexts.

- ☯ (Yin Yang Symbol):
Represents balance and harmony in Eastern philosophy, showing the duality of opposing forces that complement each other.

- ✝ (Christian Cross Symbol):
A symbol of Christianity, representing the crucifixion of Jesus Christ and widely used in religious practices, churches, and Christian artwork.

- ✡ (Star of David Symbol):
A six-pointed star associated with Judaism, symbolizing connection and protection in Jewish traditions.

- ☪ (Star and Crescent Symbol):
Often represents Islam and is commonly found on the flags of some Islamic countries and religious texts.

- ✿ (Flower Symbol):
Represents beauty, growth, and nature. Used in decorations, social media, and to show appreciation for nature and life.

- ☀ (Sun Symbol):
Symbolizes warmth, energy, and life. It’s used in weather forecasts, art, and expressions related to positivity and vitality.

- ☁ (Cloud Symbol):
Represents the weather, particularly cloudy days, and is also used in digital communication to show storage or mood.

- ☂ (Umbrella Symbol):
Often linked to protection from rain or used to indicate rainy weather in forecasts and messages.

- ★ (Star Symbol):
Symbolizes excellence, achievement, or quality. Commonly used in reviews, decorations, and to signify something special.

- ☆ (Hollow Star Symbol):
A variation of the star symbol often used for decoration, ratings, or marking items as notable or important.

- ✦ (Sparkle Symbol):
Represents magic, excitement, or something sparkling, frequently used in digital media to express glamour or joy.

- ❄ (Snowflake Symbol):
Represents winter, cold, and snow, often used in weather forecasts and to symbolize uniqueness as each snowflake is unique.

- ♠ (Spade Symbol):
One of the symbols in playing cards, often representing a challenging or serious aspect. Also used in designs and logos.

- ♣ (Club Symbol):
Another playing card symbol associated with luck and resilience. Used in games and decorative contexts.

- ♥ (Heart Symbol):
Symbolizes love, affection, and compassion. Commonly used in messages, cards, and decorations to express care and emotions.

Learn more helpful articles









![[ ] (Square Brackets) Symbol Name in English](http://mrmrsenglish.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/Square-brackets.png)




















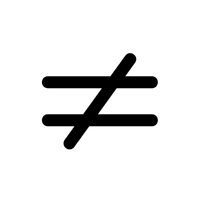
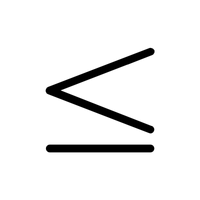




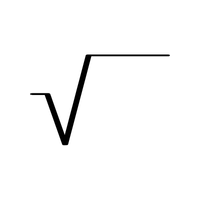



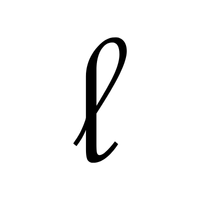




















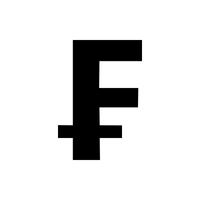


























Leave a Comment