Understanding the internal parts of the human body helps us learn how our body works and how each organ plays an important role in keeping us healthy. When we know the names and functions of these parts, it becomes easier to study science, talk to doctors, and understand health-related topics. In this article, you will learn Internal Body Parts Names in English with Images, explained in clear and easy language to support students, teachers, and beginners. This simple guide will help you learn quickly and remember each part with the help of pictures and meaningful descriptions.
All lists Internal Body Parts:
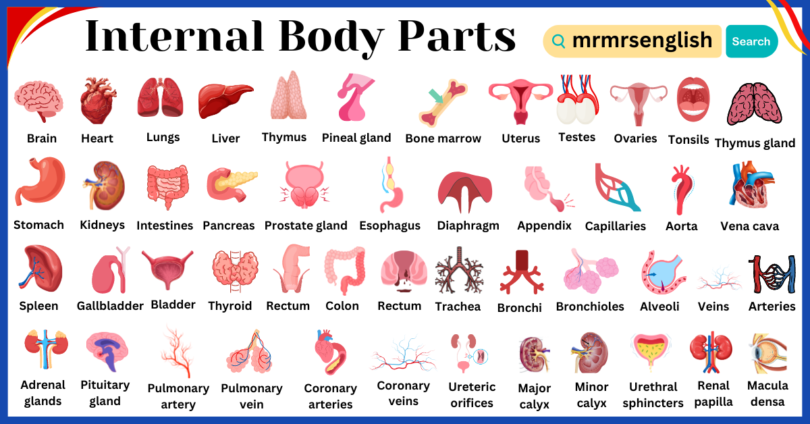
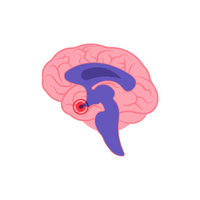
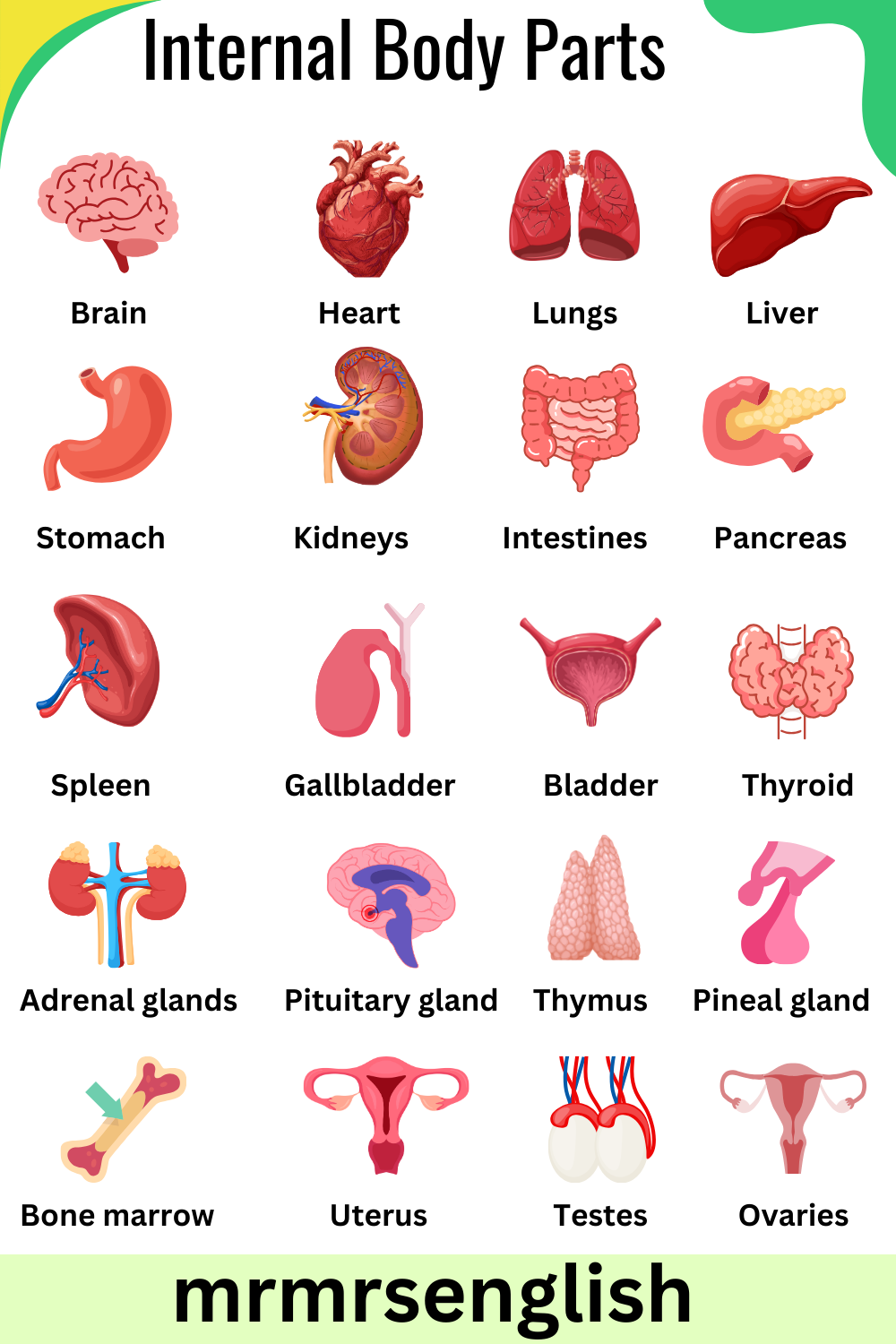
- Brain
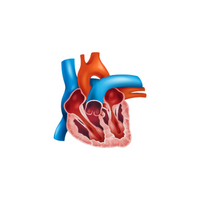
- Heart
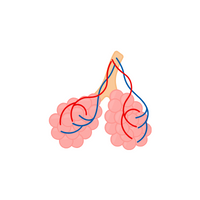
- Lungs
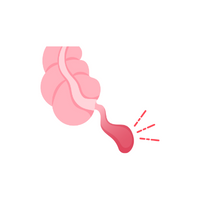
- Liver
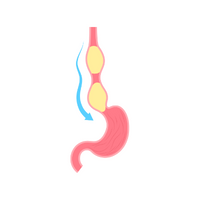
- Stomach
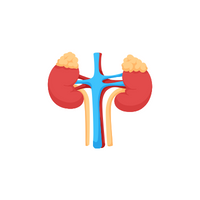
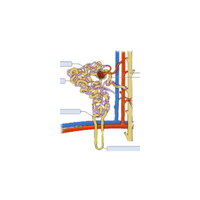
- Kidneys
- Intestines
- Pancreas
- Spleen
- Gallbladder
- Bladder
- Thyroid
- Adrenal glands
- Pituitary gland
- Thymus
- Pineal gland
- Bone marrow
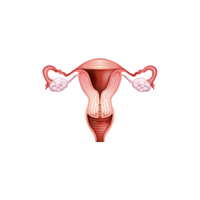
- Uterus (in females)
- Testes (in males)
- Ovaries (in females)
Internal Body Parts Names in English with pictures:
- Brain:
Body’s command center for thinking, feeling, and movement.

- Heart:
Muscle that pumps blood, delivering oxygen and nutrients.

- Lungs:
Organs for breathing, taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide.

- Liver:
Cleansing organ, filtering toxins and aiding digestion.

- Stomach:
Digestive organ, breaking down food for absorption.

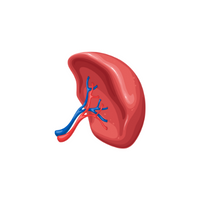
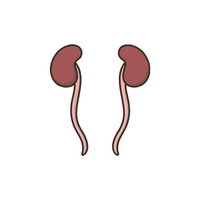
- Kidneys:
Filters waste, producing urine to remove it from the body.

- Intestines:
Tubes for digestion and nutrient absorption.

- Pancreas:
Produces insulin for blood sugar regulation and enzymes for digestion.

- Spleen:
reduces the risk of infection and removes old blood cells.

- Gallbladder:
Stores bile for digestion.

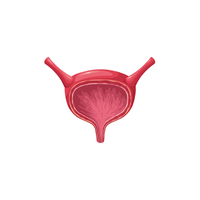
- Bladder:
Stores urine until elimination.

- Thyroid:
Produces hormones for metabolism and growth.

- Adrenal glands:
Produce hormones for stress response and blood pressure.

- Pituitary gland:
Controls other glands and bodily functions.

- Thymus:
Important for immune system function.

- Pineal gland:
Regulates sleep-wake cycles.

- Bone marrow:
Produces blood cells.

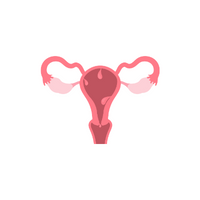
- Uterus (in females):
Where babies grow during pregnancy.

- Testes (in males):
Produce sperm and male hormones.

- Ovaries (in females):
Produce eggs and female hormones.

Internal Body Parts Names in English:
- Prostate gland (in males)
- Esophagus
- Diaphragm
- Appendix
- Rectum
- Colon
- Rectum
- Trachea
- Bronchi
- Bronchioles
- Alveoli
- Veins
- Arteries
- Capillaries
- Aorta
- Vena cava
- Pulmonary artery
- Pulmonary vein
- Coronary arteries
- Coronary veins
20 Internal Body Parts Names with Images:
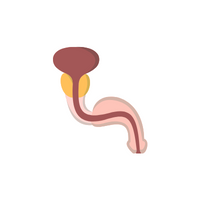
- Prostate gland (in males):
Gland in males that produces seminal fluid, aiding in sperm nourishment and transport.

- Esophagus:
Muscular tube connecting the throat to the stomach, facilitating food passage.

- Diaphragm:
Dome-shaped muscle beneath the lungs aiding in breathing by contracting and relaxing.

- Appendix:
Small pouch attached to the large intestine, playing a role in the immune system.

- Rectum:
Final section of the large intestine, storing feces before elimination.

- Colon:
Large intestine section responsible for water and salt absorption from feces.

- Trachea:
Windpipe carrying air to and from the lungs.

- Bronchi:
Tubes branching off the trachea, delivering air to the lungs.

- Bronchioles:
smaller bronchial branches seen in the lungs.

- Alveoli:
little air sacs in the lungs that are used for gas exchange.

- Veins:
Blood vessels carrying deoxygenated blood back to the heart.

- Arteries:
arteries that remove oxygenated blood from the heart.

- Capillaries:
Microscopic blood vessels connecting arteries and veins, facilitating gas and nutrient exchange.

- Aorta:
Largest artery in the body, distributing oxygenated blood to the body.

- Vena cava:
Large vein carrying deoxygenated blood from the body back to the heart.

- Pulmonary artery:
Blood vessel carrying deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs.

- Pulmonary vein:
blood vessel that travels from the lungs to the heart carrying oxygenated blood.

- Coronary arteries:
Blood vessels supplying oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle.

- Coronary veins:
Blood vessels draining oxygen-depleted blood from the heart muscle.

20 Internal Body Parts Names in English:
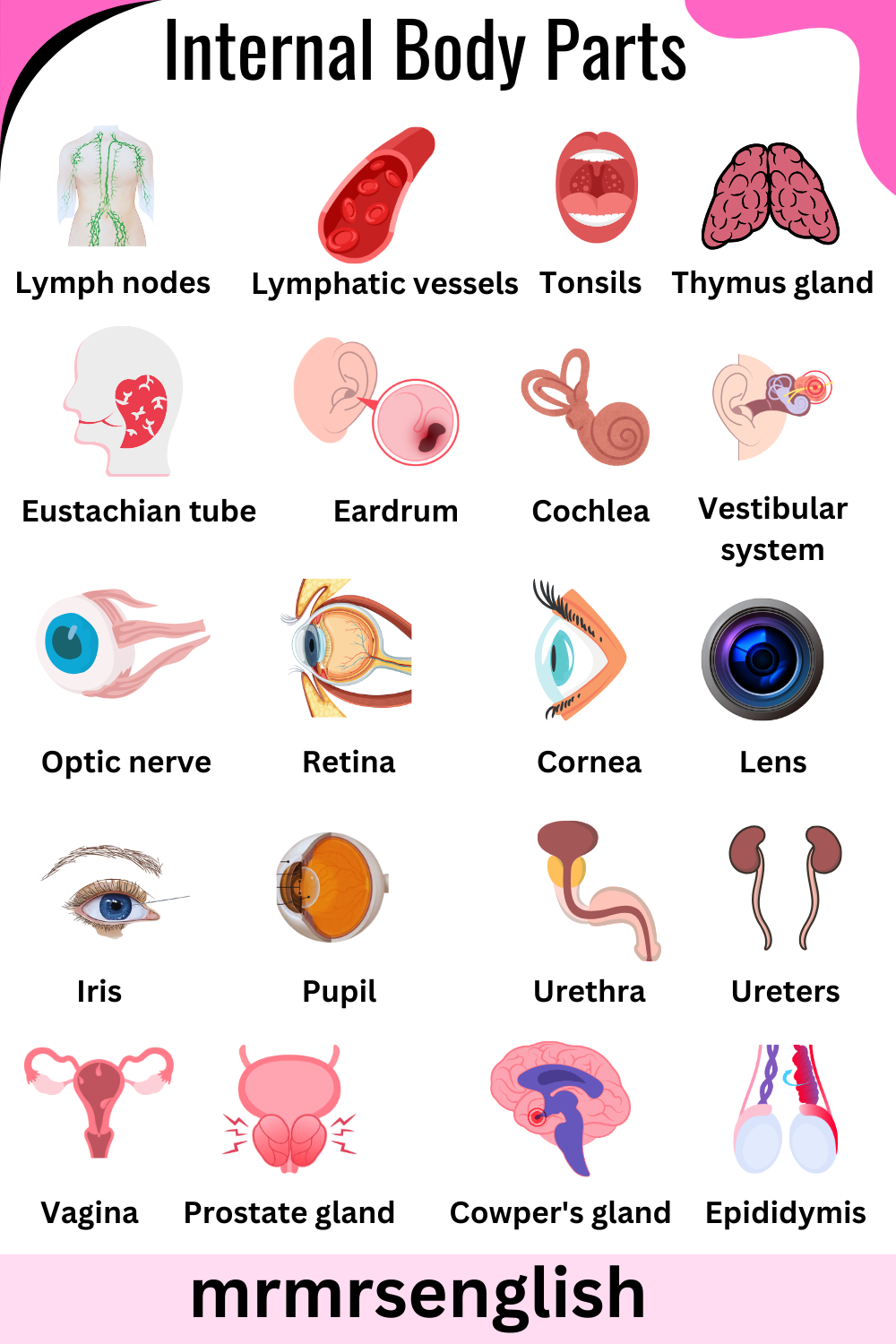
- Lymph nodes
- Lymphatic vessels
- Tonsils
- Thymus gland
- Eustachian tube
- Eardrum
- Cochlea
- Vestibular system
- Optic nerve
- Retina
- Cornea
- Lens
- Iris
- Pupil
- Urethra
- Ureters
- Vagina
- Prostate gland
- Cowper’s gland
- Epididymis
Internal Body Parts Names in English with pictures:
- Lymph nodes:
Small structures that filter lymph and aid in fighting infections.

- Lymphatic vessels:
Vessels that transport lymph, a fluid containing white blood cells, throughout the body.

- Tonsils:
Clusters of tissue in the throat that help defend against infections.

- Thymus gland:
Gland in the chest crucial for immune system development, especially in childhood.

- Eustachian tube:
Tube connecting the middle ear to the back of the nose, maintaining pressure balance.

- Eardrum:
Thin membrane separating the outer and middle ear, vibrating in response to sound.

- Cochlea:
Spiral-shaped organ in the inner ear responsible for hearing.

- Vestibular system:
Inner ear part regulating balance and spatial orientation.

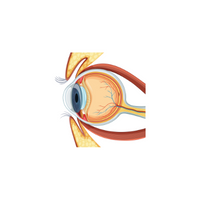
- Optic nerve:
transmits visual information from the brain to the eye.

- Retina:
Light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye containing photoreceptor cells.

- Cornea:
Transparent outer eye layer, aiding in focusing light onto the retina.

- Lens:
Clear eye structure focusing light onto the retina.

- Iris:
Colored eye part controlling pupil size and light entering.

- Pupil:
Circular opening in the center of the iris allowing light into the eye.

- Urethra:
tubes that connect the kidneys and bladder to transport pee.

- Ureters:
tubes that connect the bladder to the kidneys to transport urine.

- Vagina:
Muscular canal in females connecting the uterus to the outside and involved in reproduction.

- Prostate gland:
Gland in males producing seminal fluid for sperm nourishment and transport.

- Cowper’s gland:
Glands in males secreting fluid to lubricate and neutralize urethral acidity.

- Epididymis:
Each testicle has a coiled tube behind it where mature sperm are kept.

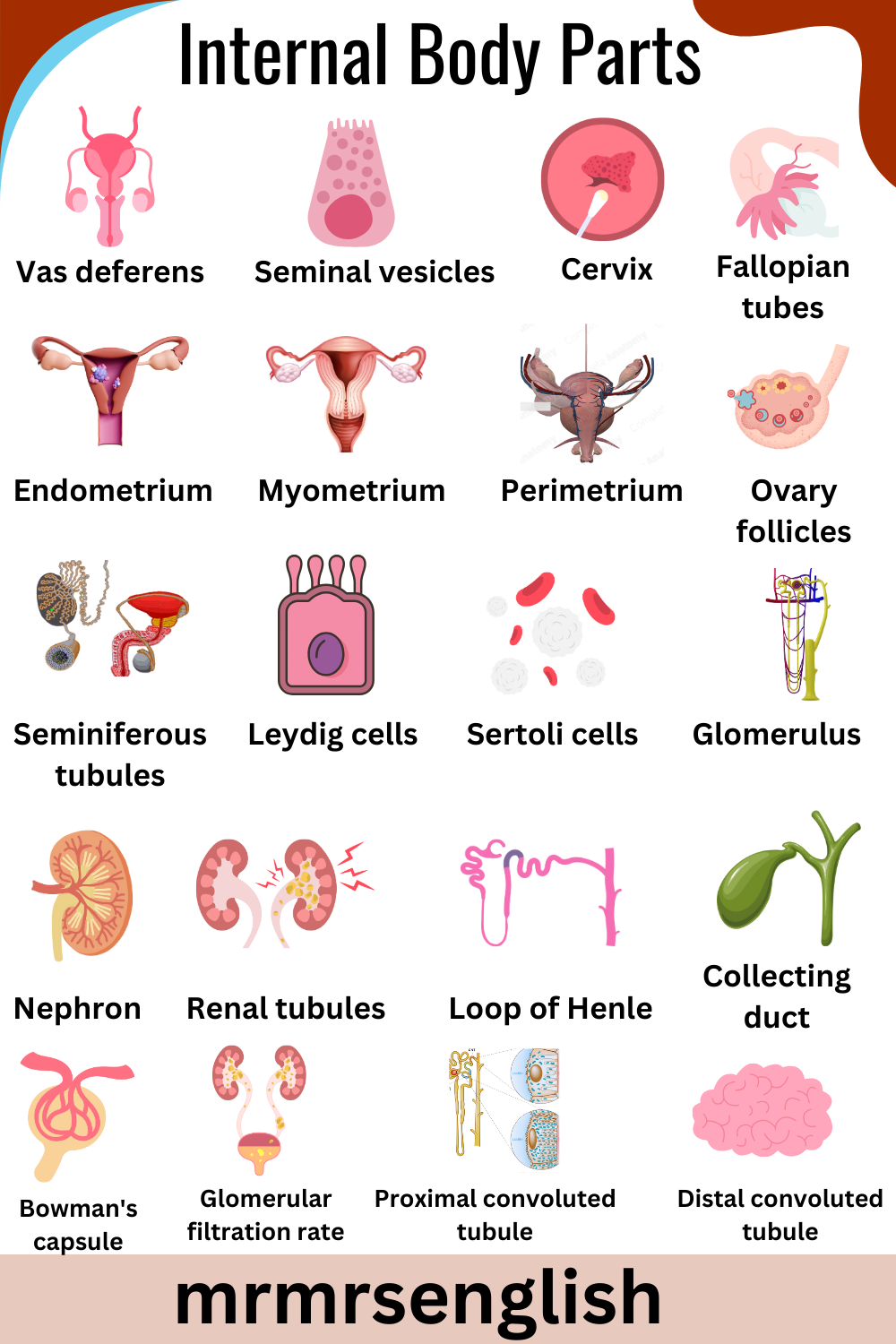
- Vas deferens
- Seminal vesicles
- Cervix
- Fallopian tubes
- Endometrium
- Myometrium
- Perimetrium
- Ovary follicles
- Seminiferous tubules
- Leydig cells
- Sertoli cells
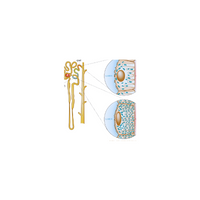
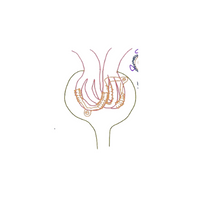
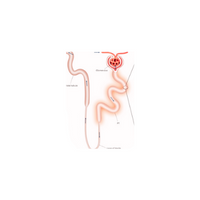
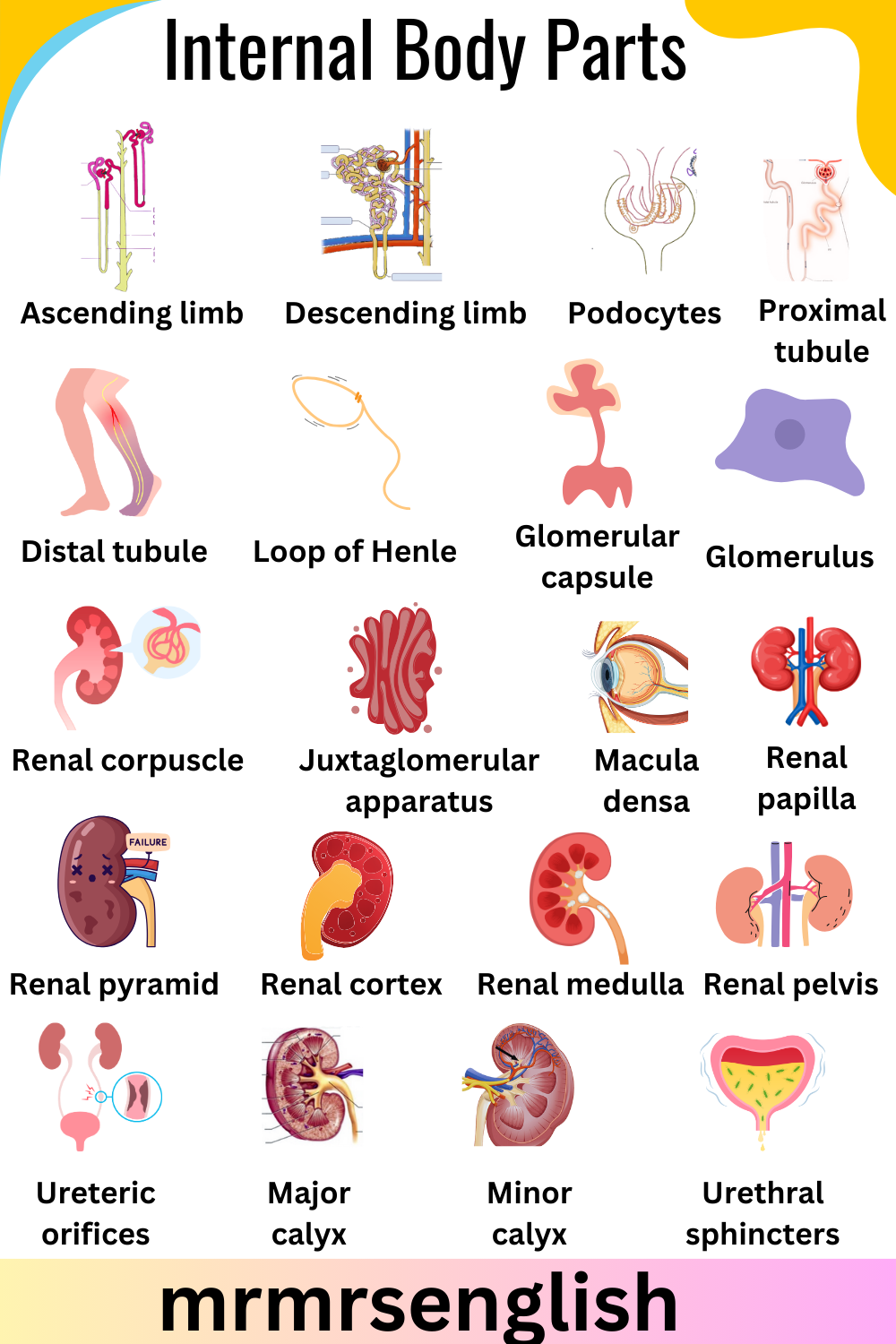
- Glomerulus
- Nephron
- Renal tubules
- Loop of Henle
- Collecting duct
- Bowman’s capsule
- Glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- Distal convoluted tubule
Human Internal body parts pictures:
What are the 10 internal parts of the body?
- Ascending limb
- Descending limb
- Podocytes
- Proximal tubule
- Distal tubule
- Loop of Henle
- Glomerular capsule
- Glomerulus
- Renal corpuscle
- Juxtaglomerular apparatus
- Macula densa
- Renal papilla
- Renal pyramid
- Renal cortex
- Renal medulla
- Renal pelvis
- Ureteric orifices
- Major calyx
- Minor calyx
- Urethral sphincters
Internal body parts names in English with images:
Learn more helpful articles












































Leave a Comment