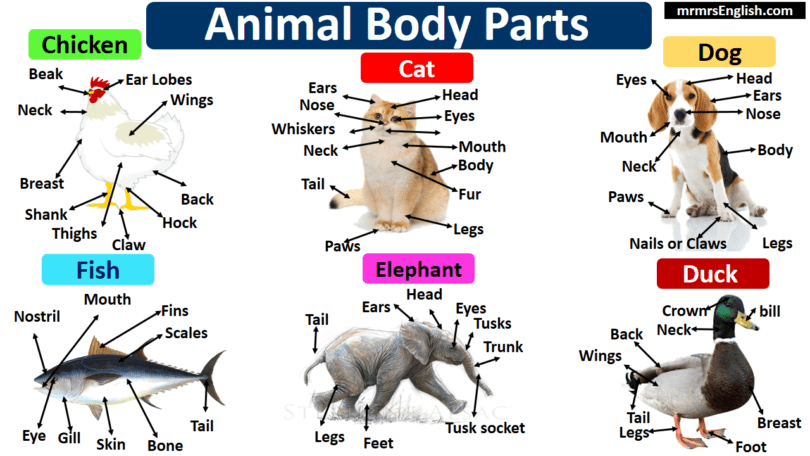
Animal Body Parts in English
Animal body parts serve various functions and are adapted to the specific needs and habitats of different species. The head typically houses sensory organs such as eyes, ears, and nose, crucial for survival and interaction with the environment.
List of Animals Body Parts
- Cat
- Dog
- Duck
- Horse
- Chicken
- Fish
- Elephant
Cat Body Parts list
Cats, independent and agile, feature distinctive body parts. Their heads hold eyes, ears, and a nose for hunting. Sharp retractable claws are on their paws, and their flexible bodies have tails for balance. Cats groom using tongues equipped with tiny spines. Known for their varied breeds, cats make adaptable and affectionate pets.
- Head
- Eyes
- Ears
- Nose
- Mouth
- Whiskers
- Neck
- Body
- Legs
- Paws
- Tail
- Fur
Parts of a Cat
- Head:
The top part of a cat’s body contains the brain and facial features like the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth.

- Eyes:
Organs on a cat’s face allowing them to see.

- Ears:
Structures on the sides of a cat’s head aiding in hearing.

- Nose:
The central part of a cat’s face is used for smelling and breathing.

- Mouth:
The opening on a cat’s face for eating, drinking, and vocalizing.

- Whiskers:
Long, sensitive hairs on a cat’s face helping them sense their surroundings.

- Neck:
The part of a cat’s body connecting the head to the rest of the body.

- Body:
The main part of a cat’s physical structure contains organs and limbs.

- Legs:
Limbs cats use for walking and running.

- Paws:
Soft, padded feet cats use for walking, climbing, and hunting.

- Tail:
A long, flexible appendage extending from a cat’s back used for balance and communication.

- Fur:
The soft, dense covering of hair keeps a cat warm and protects their skin.

Dog Body Parts list
Dogs have heads with sensory organs, four legs with paws, and tails for communication. Diverse breeds showcase unique traits, making them versatile companions and workers.
- Head
- Eyes
- Ears
- Nose
- Mouth
- Teeth
- Tongue
- Neck
- Body
- Legs
- Paws
- Tail
- Fur or Coat
- Paw Pads
- Nails or Claws
Parts of a Dog
- Head:
The upper part of a dog’s body contains the brain and sensory organs like the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth.

- Eyes:
Organs on a dog’s face enabling them to see.

- Ears:
Structures on the sides of a dog’s head used for hearing.

- Nose:
The central part of a dog’s face is used for smelling and breathing.

- Mouth:
The opening on a dog’s face is used for eating, drinking, and vocalizing.

- Teeth:
Hard structures in a dog’s mouth used for chewing and biting.

- Tongue:
A muscular organ in a dog’s mouth used for tasting, licking, and grooming.

- Neck:
The part of a dog’s body connecting the head to the rest of the body.

- Body:
The main part of a dog’s physical structure contains organs and limbs.

- Legs:
Limbs dogs use for walking, running, and jumping.

- Paws:
The padded feet of a dog used for walking, running, and digging.

- Tail:
A flexible appendage extending from a dog’s back used for balance and communication.

- Fur or Coat:
The dense covering of hair on a dog’s body provides insulation and protection.

- Paw Pads:
The soft, cushioned pads on the underside of a dog’s paws.

- Nails or Claws:
Hard structures on the tips of a dog’s toes are used for traction, digging, and defense.

Duck Body Parts list
Ducks have streamlined bodies, webbed feet for swimming, and bills designed for feeding. Waterproof feathers aid buoyancy, while wings enable flight. Their adaptable anatomy suits their semi-aquatic lifestyle.
- Breast
- Legs
- Wings
- Thighs
- Drumsticks
- Neck
- Back
- Foot
- Crown
- Bill
- Tail
Parts of a Duck
- Breast:
The front part of a duck’s body where breast meat is located.

- Legs:
Limbs ducks use for walking and swimming.

- Wings:
Appendages on a duck’s body used for flying.

- Thighs:
The upper part of a duck’s leg.

- Drumsticks:
The lower part of a duck’s leg, often used for meat.

- Neck:
The part of a duck’s body connecting the head to the rest of the body.

- Back:
The upper part of a duck’s body behind the neck.

- Foot:
The webbed, often orange-colored appendage at the end of a duck’s leg.

- Crown:
The raised, fleshy area on top of a duck’s head.

- Bill:
The elongated, pointed structure extending from a duck’s face used for feeding and grooming.

- Tail:
The flexible appendage extending from the back of a duck’s body is used for balance and propulsion in water.

Horse Body Parts list
Horses have heads with sensory organs, powerful bodies, and legs with hooves for varied activities. Their anatomy suits roles like riding and racing.
- Neck
- Shoulder
- Back
- Legs
- Muzzle
- Forehead
- Heel
- Dock
- croup
- Hook
- Knee
- pol
- Gaskin
Parts of a Horse
- Neck:
The part of a horse’s body connecting the head to the rest of the body.

- Shoulder:
The area of the horse’s body between the neck and the foreleg.

- Back:
The upper part of a horse’s body behind the withers.

- Legs:
The limbs of a horse used for walking, running, and support.

- Muzzle:
The part of a horse’s head containing the nostrils and mouth.

- Forehead:
The area of a horse’s head above the eyes.

- Heel:
The back part of a horse’s foot, above the hoof.

- Hoof:
The hard covering on the bottom of a horse’s foot.

- Dock:
The part of a horse’s tail where it attaches to the body.

- Hook:
The point of the horse’s hip.

- Knee:
The joint in a horse’s front leg, similar to a human’s knee.

- Pol:
The area of a horse’s leg above the knee or hock.

- Gaskin:
The muscular area of a horse’s hind leg between the stifle and the hock.

























































Leave a Comment